[너비우선탐색#2] 백준 2667번: 단지 번호 붙이기 JAVA
2021. 11. 1. 19:05
2667번: 단지번호붙이기
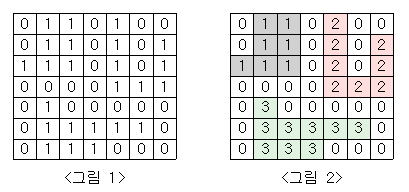
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여
www.acmicpc.net
문제
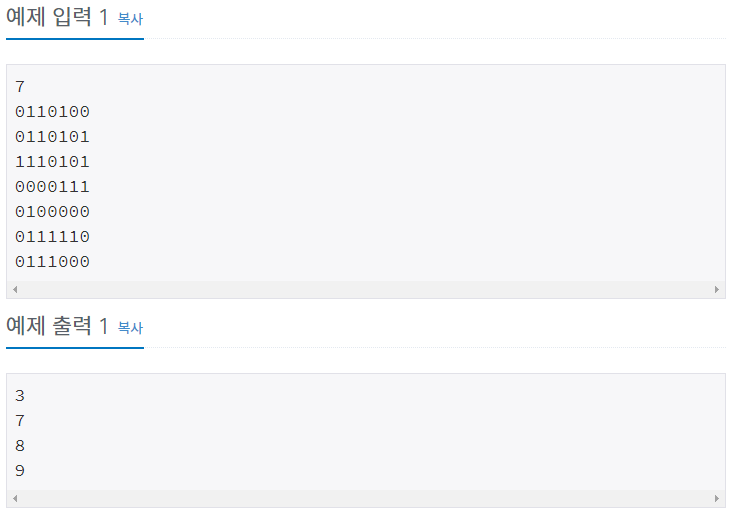
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다. 지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫 번째 줄에는 지도의 크기 N(정사각형이므로 가로와 세로의 크기는 같으며 5≤N≤25)이 입력되고, 그 다음 N줄에는 각각 N개의 자료(0혹은 1)가 입력된다.
출력
첫 번째 줄에는 지도의 크기 N(정사각형이므로 가로와 세로의 크기는 같으며 5≤N≤25)이 입력되고, 그 다음 N줄에는 각각 N개의 자료(0혹은 1)가 입력된다.
예제입출력
풀이
이번 문제는 dfs, bfs로 풀 수 있는 문제이다. 하지만 너비우선탐색 알고리즘으로 분류되어 있어서 너비우선탐색으로 풀게 되었다. 문제 특성상 한번의 큐를 돌리는게 아니라 단지의 수만큼 큐를 돌리게 된다.
소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.*;
public class Main2 {
static int n;
static int [][] map;
static boolean [][] visited;
static int count;
static List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new int[n+1][n+1];
visited = new boolean[n+1][n+1];
for(int i=1; i<n+1; i++) {
String[] str = br.readLine().split("");
for(int j=1; j<n+1; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(str[j-1]);
}
}
int totalCount = 0;
for(int i=1; i<n+1; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<n+1; j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 1 && visited[i][j] == false) {
dfs(i, j);
totalCount++;
}
}
}
Collections.sort(list);
bw.write(totalCount + "\n");
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
bw.write(list.get(i) + "\n");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
static void dfs(int x, int y) {
Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Point(x, y));
visited[x][y] = true;
int count = 1;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Point point = q.poll();
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = point.x + dx[i];
int ny = point.y + dy[i];
if(nx>0 && nx<n+1 && ny>0 && ny<n+1) {
if(map[nx][ny] == 1 && visited[nx][ny] == false) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
q.offer(new Point(nx, ny));
count++;
}
}
}
}
list.add(count);
}
static class Point{
private int x;
private int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}'Coding Test > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [깊이우선탐색#1] 백준 2667번: 단지번호붙이기 JAVA (0) | 2021.11.07 |
|---|---|
| [너비우선탐색#3] 백준 2606번: 바이러스 JAVA (0) | 2021.11.01 |
| [너비우선탐색#1] 백준 2178번: 미로 탐색 JAVA (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| [정렬#4] 백준 10989번: 수 정렬하기 3JAVA (0) | 2021.08.18 |
| [정렬#3] 백준 1427번: 소트인사이드 JAVA (0) | 2021.08.18 |





